Effective communication is key to building and maintaining strong relationships, both personal and professional. Understanding the differences between assertive and aggressive communication styles is crucial for effective communication and relationship management.
In this blog post, we will explore the concept of assertive vs aggressive communication, exploring their definitions, characteristics, and the impact they have on our interactions with others.
By gaining a deeper understanding of these communication styles, we can enhance our communication skills, foster healthier relationships, and create a more positive and harmonious environment.
Jump To Section
What is Assertive Communication?
Assertive communication is a communication style that involves expressing oneself confidently and openly while being respectful of others’ needs and opinions. This communication style is based on mutual respect and involves being clear and direct about one’s thoughts and emotions. Assertive communicators are not afraid to speak their minds and are willing to stand up for their beliefs while still being open to compromise.
Key characteristics of assertive communicators:
Some of the key characteristics of assertive communicators include:
- Direct and clear communication: They use clear language and straight-to-the-point messages.
- Confidence: They demonstrate confidence in themselves and their abilities.
- Respectful: They respect the needs and opinions of others.
- Active listening: They listen to others and make an effort to understand their perspectives.
- Non-judgmental: Assertive communicators are objective, and they do not make judgments.
Benefits of Assertive Communication
Adopting an assertive communication style can bring numerous benefits to individuals, relationships, and overall well-being. Let’s explore some of the advantages of assertive communication:
1. Enhanced Self-Confidence:
Assertive communication allows individuals to express their thoughts, needs, and opinions assertively and with confidence. It empowers individuals to assert themselves without feeling submissive or aggressive, resulting in increased self-assurance and self-esteem. As individuals become more comfortable with assertive communication, they are more likely to take initiative, set boundaries, and advocate for their needs.
2. Improved Relationships:
Assertive communication fosters healthy and positive relationships. By expressing thoughts, feelings, and needs honestly and respectfully, individuals create an open and trustworthy atmosphere. This style of communication encourages active listening, understanding, and empathy, leading to improved connection and trust with others. Assertive individuals are also better equipped to address conflicts and resolve issues constructively without damaging relationships.
3. Effective Conflict Resolution:
An assertive communication style is crucial in resolving conflicts productively. It allows individuals to express their perspective, listen to others’ viewpoints, and work towards mutually beneficial solutions. By demonstrating respect and understanding during conflict discussions, assertive communicators can de-escalate tension and avoid aggressive or passive-aggressive behavior. This, in turn, creates an environment conducive to problem-solving and compromise.
4. Promotes Collaboration and Cooperation:
Assertive communication encourages collaboration and cooperation among individuals. By valuing others’ opinions and input, assertive communicators create an atmosphere that promotes teamwork and shared decision-making. In group settings, assertive individuals are more likely to engage in active participation, generate diverse ideas, and foster an inclusive environment where everyone feels heard.
5. Reduces Stress and Anxiety:
Choosing assertive communication over aggressive or passive communication styles can reduce stress and anxiety. Assertive individuals effectively express their thoughts and needs, which minimizes misunderstandings and frustrations. By communicating assertively, individuals build confidence, engage in healthier self-expression, and establish clear boundaries, alleviating the emotional burden associated with suppressed thoughts and emotions.
6. Assertiveness as a Leadership Skill:
Assertive communication is an essential skill for effective leadership. Assertive leaders inspire trust, promote open communication, and encourage innovation and collaboration within their teams. By communicating assertively, leaders establish a supportive and respectful environment that motivates team members, improves morale, and enhances overall productivity.
What is Aggressive Communication?
Aggressive communication, on the other hand, is a style of communication that involves expressing one’s thoughts, feelings and needs in a forceful and often dominating manner. It can involve shouting, interrupting, and verbally attacking others, disregarding their rights and opinions. Aggressive communication aims to win arguments and assert dominance, often at the expense of other’s feelings and the overall quality of the interaction.
The Negative Impact of Aggressive Communication:
Aggressive communication can have detrimental effects on relationships and the well-being of the individuals involved. When individuals communicate aggressively, it can create an atmosphere of fear, hostility, and resentment. This type of communication often leads to strained relationships, decreased trust, and difficulty in resolving conflicts productively. Moreover, aggressive communication can have severe long-term consequences, including damaged self-esteem and emotional well-being for both the aggressor and the recipient of such communication.
The Difference between Assertive and Aggressive Communication
The fundamental difference between assertive and aggressive communication lies in their underlying motivations, approach, and impact on individuals and relationships.
Approach:
Assertive communication focuses on expressing one’s thoughts, feelings, and needs in a direct, clear, and respectful manner. It involves open and honest expression while considering the rights and opinions of others.
Aggressive communication, on the other hand, stems from a desire for dominance and control. It involves expressing one’s thoughts, feelings and needs forcefully and often at the expense of others’ feelings and opinions. Aggressive communicators often resort to shouting, interrupting, blaming, and verbally attacking others to assert their dominance.
Motivation:
Assertive communication aims to create a balanced and mutually respectful conversation where all parties feel heard and understood. It seeks to find a middle ground and a win-win situation through effective problem-solving and compromise.
Aggressive communication, on the other hand, is motivated by a need to “win” arguments or assert power over others. This communication style often prioritizes personal needs and desires over the well-being and opinions of others.
Impact on Relationships:
Assertive communication fosters positive and healthy relationships based on mutual respect, understanding, and effective communication. It encourages open dialogue, constructive feedback, and active listening, leading to deeper connections and trust.
Aggressive communication, however, creates an atmosphere of fear, hostility, and resentment. It damages relationships, erodes trust, and creates barriers to effective communication. Aggressive communicators may intimidate, belittle, or dismiss the thoughts and feelings of others, ultimately hindering the development of meaningful connections.
Emotional Well-being:
Assertive communication promotes emotional well-being by allowing individuals to express their thoughts and feelings honestly and assertively, which in turn leads to improved self-esteem, self-confidence, and self-respect.
Aggressive communication, on the other hand, can have severe negative impacts on both the aggressor and the recipient. Those who communicate aggressively often experience high levels of stress, anger, and frustration. Recipients of aggressive communication may suffer from diminished self-esteem, anxiety, and emotional distress.
Examples of Assertive and Aggressive Phrases in Different Scenarios:
To grasp the differences more clearly, let’s consider some examples of assertive and aggressive phrases in different scenarios:
Scenario 1:
Assertive: “I feel overwhelmed with my workload. Can we discuss ways to redistribute tasks to ensure a more balanced workload?”
Aggressive: “You always give me too much work! This is ridiculous and unfair!”
Scenario 2:
Assertive: “I appreciate your concern, but I would prefer to handle this situation on my own.”
Aggressive: “Mind your own business! I don’t need your help!”
In both scenarios, assertive communication conveys the speaker’s thoughts and feelings while maintaining respect for the other person. The aggressive communication, however, involves blame, criticism, and an attempt to dominate the conversation.
The effects of assertive and aggressive communication on interpersonal relationships and personal well-being are significant. It is important to recognize and choose assertive communication over aggressive communication to foster healthy and positive connections with others.
Tips to Become a More Assertive Communicator
Mastering assertive communication requires practice and a willingness to make changes in how we express ourselves. Here are some practical tips to help you become a more assertive communicator:
1. Recognize and acknowledge your feelings:
Start by tuning into your emotions and understanding how you truly feel about a situation. Take the time to identify your thoughts and emotions, as this self-awareness will provide a foundation for assertive communication. Acknowledge your rights to have feelings and opinions without judgment.
2. Use “I” statements:
When expressing your thoughts or needs, use “I” statements to take ownership of your feelings and avoid sounding accusatory. For example, instead of saying, “You never listen to me,” you can say, “I feel unheard when I’m interrupted during our conversations.”
3. Be direct and clear:
Clearly articulate your thoughts, needs, and boundaries without beating around the bush. Avoid passive or passive-aggressive language that may lead to misunderstandings. State your point directly, respectfully, and assertively.
4. Practice active listening:
To build effective communication, actively listen to others without interrupting or planning your response. Show genuine interest and validate their feelings, which will facilitate constructive dialogue and understanding.
5. Set boundaries:
Establishing personal boundaries is essential for assertive communication. Let others know about your limits, and communicate those boundaries respectfully. This will help prevent others from overstepping or disrespecting your space, while also fostering open and reciprocal communication.
6. Use assertive body language:
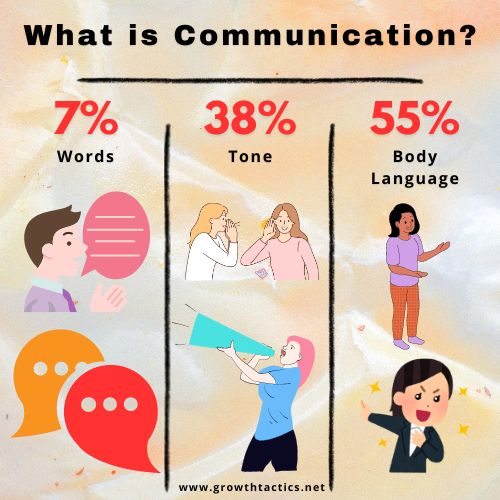
Your body language plays a crucial role in assertive communication. Maintain good eye contact, stand or sit up straight, and use confident and composed gestures. This sends a message that you are attentive, self-assured, and open to discussion.
7. Practice assertiveness in low-stakes situations:
Begin by practicing assertive communication in less challenging situations. Engage with supportive friends or colleagues to practice expressing your thoughts and needs confidently. Gradually, you can apply these skills to more challenging conversations.
8. Reframe negative thoughts:
When faced with self-doubt or negative thoughts about being assertive, challenge and reframe them. Replace thoughts like “I don’t want to upset anyone” with “It’s important for me to express myself respectfully and honestly.”
9. Accept pushback:
In assertive communication, it is natural to face pushback or disagreement. Accept that others may not always agree with your perspective or needs. Respect their viewpoint, and be open to finding common ground or compromise.
10. Practice self-care:
Maintaining assertive communication requires self-care and self-compassion. Take care of your physical and emotional well-being, seek support from trusted individuals, and practice techniques such as mindfulness or stress reduction strategies.
Conclusion
Becoming a more assertive communicator is a journey that requires practice and self-reflection. By recognizing and acknowledging your feelings, using “I” statements, and setting clear boundaries, you can gradually develop assertive communication skills. With consistent effort and patience, you can become an effective assertive communicator and build healthier relationships based on respect and understanding.


