Risk is an important part of getting ahead in life. If you don’t take any, you will likely end up never getting ahead. But how do you know which are worth taking?
The answer is identifying and understanding risk. The risk management tools and techniques listed below will help you identify and understand what you are dealing with.
When we think of risk analysis, we think of businesses or finance. But utilizing risk management in every aspect of your life is important.
Assessing risk properly and efficiently is the difference between success and failure. Have you ever seen somebody that just seems lucky? Often, it’s not luck. They are just good at making the right decisions and risk management has a lot to do with that.
Continue reading to learn how to use these quick and effective risk management tools to put yourself in the best situations.
Jump To Section
What Is Risk Management?
Risk management is the act of identifying, analyzing, and controlling risks. These risks can be anything from physical harm to monetary losses to harm to credibility. A solid risk management plan will help you avoid the negative effects of problems.
A risk analysis factor is a problem or issue that could arise when taking a risk. These factors are used to decide if a risk is worth taking. We will discuss how to use these risk factors to determine the value of the risk later.
Risk consists of two parts: The probability of a problem occurring and the negative effects of the problem if it occurs. When you think about risk management, you should also be thinking about rewards. The reward is what can be gained if everything goes well.
Types of Risk
There are three main types of risk:
Internal risk: Internal risk is the type of risk that arises within your organization, such as a failure to comply with government regulations. While you can’t control all external factors, you can control your own actions, so this is something you must address internally.
External risk: External risk is the type of risk that arises from outside your organization, such as natural disasters or changes in the market. These are things you cannot control, but they can have a huge impact on your company’s future if not addressed properly.
Structural risks: Structural risks are those that arise due to the structure of your company or industry itself—they aren’t necessarily caused by an individual or group’s actions or decisions within the company itself (though they may be).
When Should We Use Risk Analysis?
You should be using risk analysis in every portion of your life. On a daily basis, you face some sort of risk. Some of these risks are bigger and more important than others but the more risk analysis you perform, the more success you will see.
Quantitative Risk Analysis
Quantitive risk analysis is simply adding a numeric value to risk. For example, a particular risk has a 5 out of 10 chance of occurring and a 5 out of 10 severity. So, this risk would be assigned a value of 5.
This can be very useful if you assign a quantitative value to the reward. Using the same risk above we can look at the reward side of it. The reward has a 5 out of 10 chance of occurring. The reward is huge, so it has an 8 out of 10 impact. That would put the quantitive value for this risk at 6.5. So, in this scenario, the reward is worth the risk.
This can be very useful in step 2 of the risk analysis process we discuss later.
Project Risk Analysis
Project risk analysis is an extremely important part of the project planning process. If you don’t analyze the risks involved in any project you will be setting yourself up for failure.
Finding Risk Analysis Factors – Risk Analysis Process
- Step 1 Identify
The first step is to identify your risk. In this step, you want to gain as much information about your situation as possible. The more information you gather, the better your decision will be.
- Step 2 Risk Vs. Reward
In this step, you want to think about the pros and cons. Make a list of what pros and cons are included with the risk. Assign a probability to each pro and con. I prefer to use the 1-10 scale, because it’s easy to work with.
- Step 3 Decide
Now is the time to decide if the reward is worth the risk. Look at your pros and cons list and use that as a reference to make your decision. First, determine if there is a con that is a deal-breaker. For example, you may be thinking about doing something that could make you a millionaire. But there is a medium chance that you could lose everything. That risk may not be worth the reward.
Looking at your list, are there ways to minimize risk without giving up the reward? This can help make your decision a little easier. As for the risks that do remain, start devising plans to handle them if the problem occurs.
- Step 4 Monitor
After you decide that the risk is worth the reward, it’s time to monitor your decision. Since you have prepared at least mentally for problems, you should be ready for them. Look for warning signs that the risk isn’t working out.
Risk Management Tools List
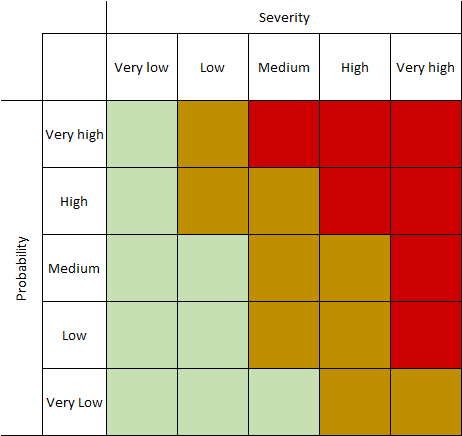
1. Risk Analysis Matrix
A risk assessment matrix is a simple tool used to help determine if a risk is worth it. As you can see from the example below, it contains a likelihood on one side and the severity of the risk on the other. For example, if something falls into the high probability/high impact category, you should avoid that.
Risk Analysis Matrix Example
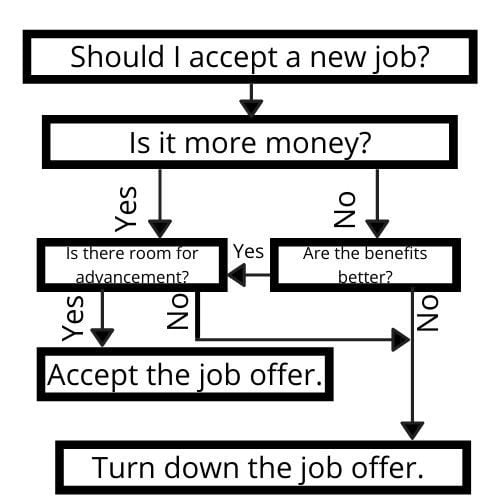
2. Decision Tree
A decision tree is a flow chart that uses a series of questions or choices that branch out into various outcomes. This can be useful in determining risks and the best course of action.
Decision Tree Example:
3. Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
This tool is useful in determining all the potential failures in a process or product. This will help you map out how severe the risk is and how probable it is.
The area this model will help you explore are:
- What could go wrong?
- What would cause this failure to happen?
- What will be the effects of this failure?
For more information on FEMA check out this great article.
4. Bowtie Model
A Bowtie Model is useful for risk management. You start with the potential risk or problem in the center of the bowtie. On the left, you put actions you can take to prevent the problem. On the right, you put actions you can do to recover if the risk or problem arises.
Absolutely! I’d love to guide you through how to use each of these risk management tools. I’ve used them all in my own projects, and I’ll share some personal tips along the way. Remember, there’s no one right way to use these tools. Feel free to adapt them to fit your unique needs.
5. Monte Carlo Simulation
To perform a Monte Carlo Simulation:
- List all your variables (like cost, time, resources).
- Assign a range of possible values to each variable.
- Use a computer program to run thousands of random scenarios.
- Analyze the results to see the most likely outcomes.
I once used this to predict project timelines. It helped me spot potential delays I hadn’t even considered!
6. Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram)
Here’s how to create a Fishbone Diagram:
- Write your main problem at the “head” of the fish.
- Draw “bones” branching out from the spine.
- Label each bone with a category (like People, Process, Equipment).
- Add smaller bones with specific causes in each category.
- Discuss and analyze the results with your team.
I love using this in brainstorming sessions. It gets everyone thinking creatively about problems.
7. SWOT Analysis

To do a SWOT Analysis:
- Draw a square divided into four boxes.
- Label them Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
- Fill each box with relevant points.
- Review and discuss the results.
- Use this info to make action plans.
I do a personal SWOT analysis every year. It’s a great way to set goals and grow.
8. Probability and Impact Matrix
Here’s how to use this matrix:
- List all your potential risks.
- Score each risk on probability (how likely it is to happen).
- Score each risk on impact (how bad it would be if it did happen).
- Plot each risk on a grid based on these scores.
- Focus on the risks in the high probability, high impact quadrant.
This tool has saved me from wasting time on minor risks and helped me focus on what really matters.
9. Risk Register
To create a Risk Register:
- Make a spreadsheet or table.
- List all identified risks.
- Add columns for impact, probability, mitigation plans, and owners.
- Fill in the details for each risk.
- Review and update regularly.
I keep my risk register open in team meetings. It helps us stay on top of potential issues.
10. Scenario Analysis
To perform Scenario Analysis:
- Identify key factors that could change.
- Create best-case, worst-case, and most likely scenarios.
- Describe what would happen in each scenario.
- Plan how you’d respond to each one.
I’ve used this to help businesses prepare for market changes. It’s a great way to stay flexible.
11. Fault Tree Analysis
To do a Fault Tree Analysis:
- Start with the main problem at the top.
- Work downwards, adding all possible causes.
- Use logic gates to show how causes combine.
- Keep going until you reach root causes.
- Analyze to find the most critical factors.
This tool helped me prevent a major system failure once. It’s great for complex problems.
12. Event Tree Analysis
Here’s how to do an Event Tree Analysis:
- Start with an initiating event on the left.
- Branch out to the right with possible outcomes.
- Keep branching for each new possibility.
- Assign probabilities to each branch.
- Calculate the likelihood of each end result.
I use this when planning new projects. It helps me see all the possible ways things could unfold.
13. Risk Breakdown Structure (RBS)
To create an RBS:
- Start with ‘Risk’ at the top.
- Create main categories below (like Technical, Management, External).
- Break each category into subcategories.
- Keep breaking down until you reach specific risks.
- Use this structure to organize your risk management efforts.
This tool helps me make sure I’m not missing any areas of risk in my projects.
14. Delphi Technique
To use the Delphi Technique:
- Identify a group of experts.
- Ask them to anonymously answer questions about risks.
- Compile and share the results with the group.
- Have them revise their answers based on the group’s responses.
- Repeat until you reach a consensus.
I’ve used this to tackle tricky problems where no one person had all the answers.
15. Sensitivity Analysis
To perform a Sensitivity Analysis:
- Identify the key variables in your project or decision.
- Change one variable at a time.
- See how much the outcome changes.
- Repeat for all important variables.
- Identify which variables have the biggest impact.
This helps me figure out where to focus my efforts for the biggest payoff.
16. What-If Analysis
To do a What-If Analysis:
- Gather a diverse team.
- Brainstorm “What if…” questions about your project or process.
- Discuss the potential impacts of each scenario.
- Plan how you’d respond to each one.
- Use this info to improve your plans and preparations.
I love using this tool. It’s sparked some of my most creative problem-solving sessions.
Technology-based Risk Management Tools

Technology-based risk management tools are becoming increasingly popular among businesses due to their ability to automate and streamline risk management processes. These tools use advanced technologies such as predictive analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to identify, assess, and mitigate risks.
Advantages of Technology-based Risk Management Tools
One of the biggest advantages of technology-based risk management tools is their ability to provide real-time risk assessments. By analyzing large amounts of data in real time, these tools can quickly identify potential risks and provide insights into how to mitigate them. This can help businesses stay ahead of potential risks and make informed decisions to minimize their impact.
Another advantage of technology-based risk management tools is their ability to automate many of the manual processes associated with risk management. This can save businesses a significant amount of time and resources, allowing them to focus on other important tasks.
Examples of Technology-based Risk Management Tools
There are many different types of technology-based risk management tools available, each with their own unique features and benefits. Some popular examples include:
- LogicManager: A cloud-based risk management software that uses advanced analytics and automation to help businesses identify and mitigate risks.
- RiskSense: A risk management platform that uses machine learning and artificial intelligence to identify and prioritize risks based on their potential impact.
- CyberGRX: A cybersecurity risk management platform that uses data analytics and automation to help businesses assess and manage their cybersecurity risks.
Choosing the Right Technology-based Risk Management Tool
When choosing a technology-based risk management tool, it’s important to consider factors such as budget, complexity, and scalability. Businesses should also evaluate the features and capabilities of each tool to ensure that it meets their specific needs.
Overall, technology-based risk management tools can be a valuable asset for businesses looking to improve their risk management processes. By leveraging advanced technologies and automation, these tools can help businesses stay ahead of potential risks and make informed decisions to minimize their impact.
Risk Management Plan
Having a good strategy is vital to handling the effects of risk. Utilizing these risk analysis tools will help you determine if the risk is worth it. Also, you will have a plan on how to deal with the problems when they arise.
You can’t plan for everything but not having a plan is planning for failure.
Did you find this article on risk management tools useful? Please share so others can enjoy it.